
Hence, the molar mass of Na2CO3 thus becomes 106 g/mole. When we add all the totals, we get (46 + 12 + 48) = 106. To put it another way, the molar mass is the overall mass in grams of all the particles that make up a mole of a specific molecule.īecause sodium carbonate comprises 2 sodium atoms, 1 carbon atom, and 3 oxygen atoms. The molar mass of the substance refers to the mass of one mole of that material and the number of grams per mole. Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate vs.What is the molar mass of sodium carbonate na2co3?.Sodium BiCarb not decomposing as it should at 500-600F.Separate sodium bicarb from NH4CL and water.


References Relevant Sciencemadness threads
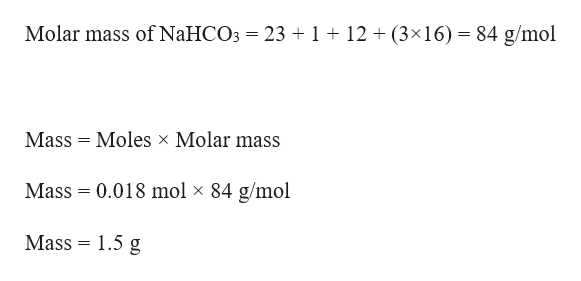
Waste sodium bicarbonate can also be used as neutralizing agent for acids and other corrosive solutions. Sodium bicarbonate can be poured down the drain or dumped in trash. Sodium bicarbonate should be stored in closed bottles away from any acidic vapors. It will also increase the sodium level in blood if large quantities are consumed. Sodium bicarbonate is non-toxic, but if swallowed it will neutralize the gastric acid and release carbon dioxide, causing burps or if too much is ingested, vomit. Sodium bicarbonate, like sodium carbonate, can be used in acid-base titrations. As many carbonates are not water-soluble, sodium bicarbonate can be used in double replacement reactions to produce the carbonates of many metals. Due to its ease of access and relative cheapness, sodium bicarbonate can be used to neutralize and clean acid spills as well it is convenient, because the reaction of neutralization in its case is endothermic and results in cooling, unlike with hydroxides, which give very exothermic reactions that may lead to boiling and sprinkling of acids. Neutralization of sodium bicarbonate with acids yields a sodium salt and large amounts of carbon dioxide reaction vessels should have ample headroom to prevent spills. Sodium bicarbonate is one of the most versatile and commonly encountered compounds in amateur chemistry. Do not boil the bicarbonate solution, as sodium bicarbonate decomposes above 50 ☌. Cool the solution until sodium bicarbonate precipitates, then filter and air dry the bicarbonate precipitate. Sodium bicarbonate can be prepared by bubbling carbon dioxide in a concentrated solution of sodium carbonate. It is essential to buy unscented baking soda, as scented baking soda may form side products with other reactants or give a nauseating odor in many reactions. Relatively pure sodium bicarbonate can be purchased in supermarkets, cheaply and in large quantities, as baking soda. It has a slightly salty taste, similar to that of sodium carbonate. Sodium bicarbonate forms white crystals and is soluble in water, but insoluble in organic solvents. Sodium bicarbonate slowly decomposes to form sodium carbonate above 50 ☌, though the rate of decomposition is much higher at or above 200 ☌.Ģ NaHCO 3 → Na 2CO 3 + H 2O + CO 2 Physical

This property allows sodium bicarbonate to be useful as a safe neutralizing agent for both acids and bases. Sodium bicarbonate reacts with bases such as sodium hydroxide to form carbonates: Sodium bicarbonate will react with acids to release carbon dioxide.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
